Softgel Versus Hard Gelatin Capsule
- by Sharry
- July 5, 2022
Softgel V.S. Hard Gelatin Capsule
Both of them belong to the solid dosage of capsules.
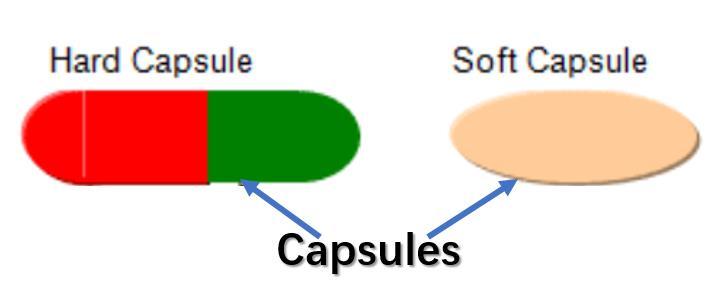
So What is Capsule?
Capsules, in medicine speaking, refers to capsules made of gelatin to contain drugs; which are used by manufacturers when the drug cannot be compacted into a solid tablet or pills. The capsule can be filled with bitter, odorous, or irritating powders to make it easier to be swallowed. Medicines or preparations in capsules are generally powders or granules that are irritating to the esophagus and gastric mucosa, or have a bad taste; Or effective ingredients that are easily volatile, easily decomposed by saliva in the oral cavity, and are riskily inhaled into the trachea. By the dosage form of capsules is not only protective of the physiological and biochemical characteristics of the drugs but also protects the digestive organs and respiratory tract of patients. They are also useful when the drug needs to be mixed with oil or other liquid to aid absorption in the body.
There are two types of capsules, hard or soft
Hard capsules, which are more commonly seen, are composed of a rigid shell in two pieces that fit and lock together and are then filled with the drug. This dosage form is normally more suitable for drug powders and can only be used if the drug will be easily dissolved in the stomach.
Soft gelatin capsules/softgel, are formed in a single piece with oils inside, such as fish oil, Omega 3,6,9, Q10; or drugs that need to be dissolved in oils or other liquids to help the drug to be absorbed in the stomach. Soft capsules shell can melt within minutes in the stomach.
So what’s the difference between softgel and hard gelatin capsule. Here we only refer to solid dosage as drug or medicine purpose instead of nutrients and supplement.
I. Filling Content difference:
Softgel: oils or liquid drugs or suspensions that do not dissolve gelatin as softgel wrapping shell.
Hard capsule: herbal material extract, medical powder or auxiliary grains, particles, pellets.
II. Outside shell
Softgel: the shell is soft with elasticity and mainly composed of gelatin, plasticizer, and water.
Hard capsules: Gelatin is the main material of hard capsules.
III. Absorption rate
Softgel: relatively easily absorbed because the shell material is easily broken down (5-10 minutes). The quicker effect, which is good for immediate pain relief;
Hard capsule: relatively harder to be absorbed and needs to stay in the stomach for a long time (about 30-60minutes).
IV. Freshness
Softgel: Keep it fresh, because it has higher water content in the shell.
Hard capsule: dry powder, easy to get wet, humidity, and caking.
V. Appearance
Softgel: colorless, light yellow, brown-yellow, black, red, and many others, etc; the shapes are also various; much wider options. The soft gel dosage selection sheet as below:
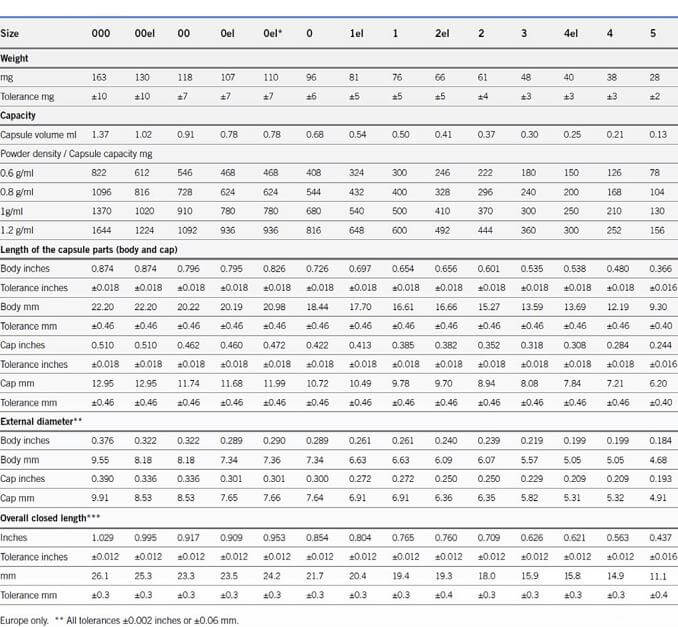
Hard capsules: colorless, single color, double color, half-transparent, half-color, etc. But shapes are always the same only difference in size, yet the sizes are also limited. The empty capsule datasheet as below:
VII. Peeling off the Shell
Softgel: You can remove the shell if you don’t care for the tastes.
Hard capsules: for certain powder inside, it is not ok to peel off the shell and take powder directly into mouth;
VIII. Stability of ingredients
Soft capsules: Most are unstable, but can be placed at room temperature, and are not easily oxidized due to hermetical sealing.
Hard capsules: generally, more stable, but sensitive to light or heat, and easily oxidized due to the capsule filling and locking system.
X. How to choose capsule products?
1. Whether it is a drug or a health care product, try to use isotonic powder, which can be absorbed 90% in 5 minutes, then consider the capsule (soft capsule first, then hard capsule), and finally consider the granule (about 1 hour);
2. If possible, choose as few colored products as possible;
3. Try to choose products that are protected from light and sealed, it is best not to buy transparent packaging;
4. If the hard capsule is flattened or deformed, it is best not to choose or eat it;
5. Generally, it can be taken with cold water or warm water, but soft capsules are generally larger. It can be bitten and swallowed (not all capsules).
XI. In addition: When people take capsules, they are prone to fall into three misunderstandings.
1. Using hot water. This will accelerate the dissolution of the capsule, and the capsule skin will easily stick to the throat or esophagus. It is best to use cold water.
2. Sitting or lying down. Some capsules are very corrosive, and if they accidentally stick to the esophagus, they will burn the esophageal mucosa. It is best to stand up.
3. Peel off the shell. For sustained-release capsules and enteric capsules; the medicine inside is more irritating to the stomach; so not suggested to peel off the shell.
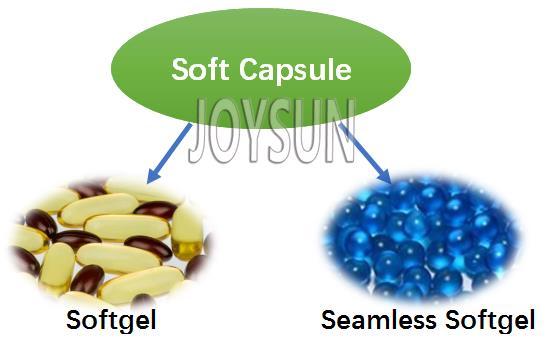
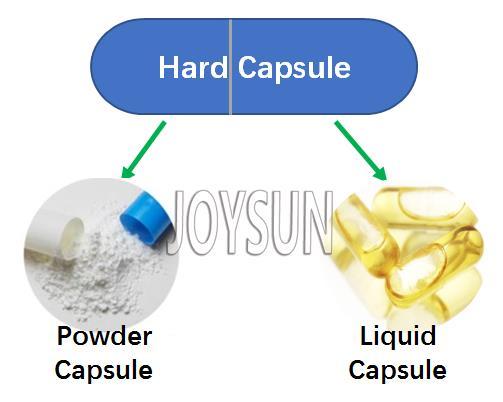
With continuous development, the softgel capsule and hard capsule can both be sub-classified into below:
Professionals in formulation try to fill the liquid or paste into empty capsule to make such dosage form more efficient.
The trends in softgel development
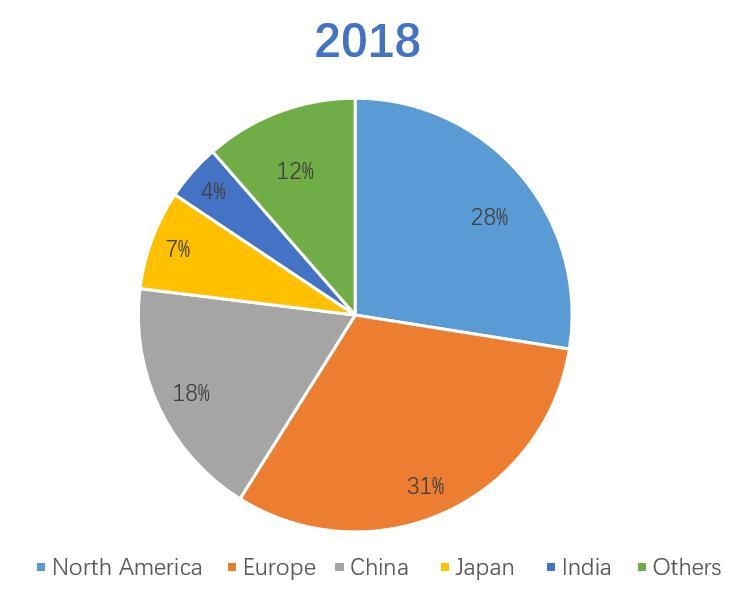
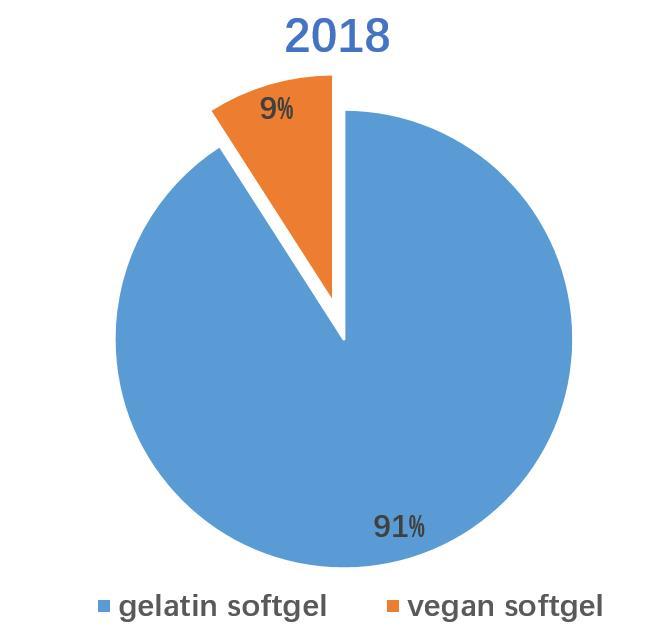
Soft capsules are mainly divided into gelatin soft capsules and non-animal soft capsules. Among them, gelatin soft capsules are the most important application type, accounting for 90.9% of the global soft capsule market in 2018. This proportion is more prominent in China, and gelatin softgels account for about 98.7% of China’s softgel market share. Vegetarian softgel is more expensive in price and more difficult in production. Currently, there are carrageenan based softgel and starch/tapioca based softgel.
The trends in hard gelatin capsule development
The capsule shell is usually called as ‘empty capsules’, according to the raw material to produce it, there can be gelatin capsules and vegetarian capsules. They cannot be distinguished by their appearance. When use capsule filling machine to fill material into empty capsules, we usually choose non-split capsules while capsule body and cap are pre-locked. The machine will operate all process from capsule body-cap separation to capsule guide, filling, locking again to discharge.
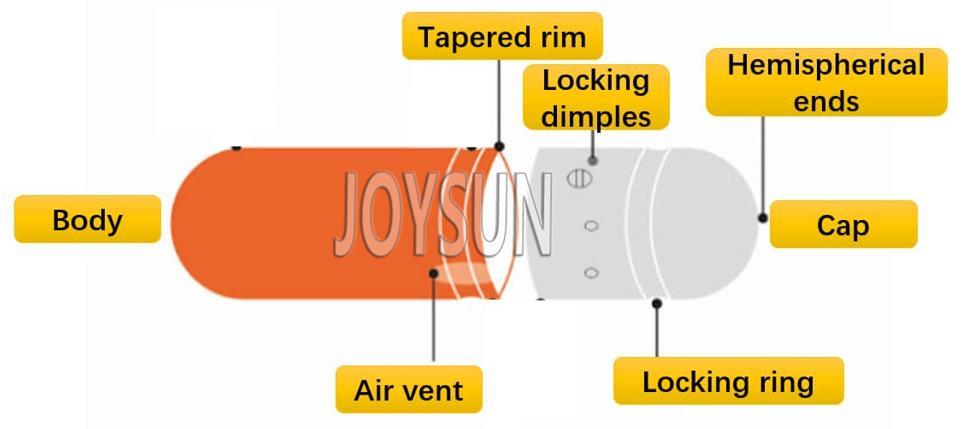
The structure of a non-split capsule is like below: six elongated locking dimples maintain precise, round capsule diameter to improve the performance of capsule filling machine; Round hemispherical ends are mechanically stronger and more resistant to deformation; Air vents allow air to escape from the cap, it is critical for high-speed capsule filling machine; locking rings to provide leakage-free closure.
Gelatin capsules are still the most widely used type. This grade of gelatin meets the stringent requirements for pharmaceutical products.
The vegetarian capsules gain more and more market share worldwide with the popularity of a healthy lifestyle, non-killing concept, and religious reasons. The outer shell is generally prepared from starch, HPMC (Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose), Pullulan (known as pollution-free plastics).
To meet the growing demand for liquid capsule products, the ‘Licaps’ liquid-filled capsule designed for the safe sealing of liquid and semi-solid capsules. Even though the conventional empty capsules can also fill with liquid with the aid of a banding machine, there is not enough data to support whether the shell will be dissolved by the inside liquid or not. There is a certain risk of leakage and dissolving problems to some materials.
The liquid capsule has many advantages: Using gelatin, plant-derived capsules in a variety of sizes and colors; Having a higher absorption rate and bioavailability than powder capsule; Safer control of highly active drugs; For low dose level capsules, it is more content uniformity, especially at low dose levels. Better sealing of cap body and cap, so better protect the ingredients from oxygen; and the inside odor can be covered better.
Whether it is the gelatin capsule or vegetarian capsule or liquid capsule, it is a food-grade material under strict standardized production, and it has no harm to the human body.
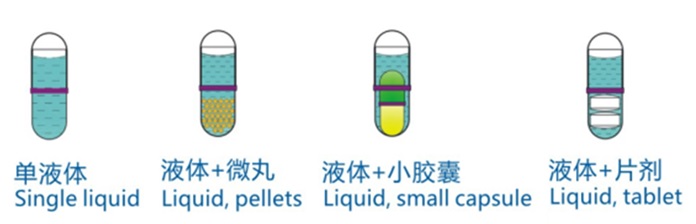
Types of liquid-filled capsules
Liquid Gel Capsule • Beadlets in Liquid Capsule • Pellets in Liquid Capsule • Capsule in Liquid Capsule
Different Machines and Formulations for each type of capsule
Softgel capsule is produced via softgel encapsulator the main principle is utilizing liquid gelatin solution‘ s elasticity and die roll cold pressing to make a 2 pieces gelatin ribbon sealed as a whole dose.
- Softgel encapsulation machine for regular gelatin softgel.
- Customized softgel encapsulation machine for regular carrageenan based softgel and starch/tapioca based softgel.
- Seamless Softgel machine to make seamless softgel.
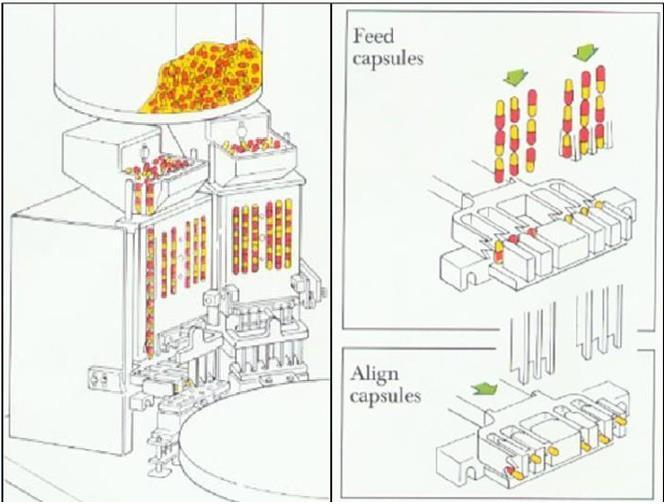
The hard capsule is finished by a capsule filling machine of manual, semi automatical or automatic encapsulators. The automatic capsule filling machine has continuous actions of capsule rectification, separation, filling, locking, and discharging step by step. By filling machine greatly improve production efficiency and reduce labor costs.
Capsules rectification→Separation of capsule cap and body→Filling→Wasted capsules rejection→Capsule locking→Filled capsuled ejection→Cleaning
- Conventional Capsule Filling Machine for powder
- Updated Liquid Capsule Filling Machine for liquid and paste